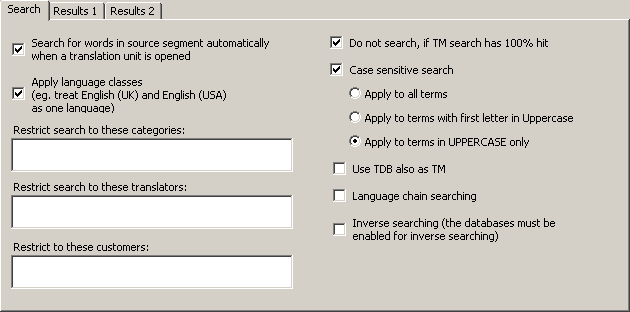
The TDB search parameters are very similar to the TM search parameters, except that there is no savings tab, because terminology is not saved automatically.
The Search tab contains the TDB search parameters:

The following settings can be made:
· Search for words in source segment automatically when a translation unit is opened:
If this checkbox is checked, MetaTexis will automatically search in the specified TDBs when a TU is opened and the translation box is empty (no translation or TM segments present).
· Do not search if TM search has 100% hit:
If this checkbox is checked, no TDB search is executed when the TM search, which is always executed before the TDB search, has a 100% hit. In this case, there is usually no need to perform a terminology search.
· Apply language classes:
If this checkbox is checked, MetaTexis looks for language classes rather than for the language defined. There are several languages that have variants. For example, there are many variants of the English, French and Spanish languages. If language classes are applied, MetaTexis treats the variants of a language as the same language, e.g. English (UK) and English (USA) are treated as one language. So, if a TDB contains segments in different languages that belong to the same language class, they are all included in the search. On the other hand, if this checkbox is unchecked, MetaTexis only includes the segments in the same language as the source language of the MetaTexis document (see Document Options).
· Restrict search to these categories:
If you enter a category in this text box, the TDB search is restricted to segments with this category. You have to be careful with this command: Make sure that the category entered actually exists in the TDBs.
If you enter more than one category, they must be separated by a semicolon.
· Restrict search to these translators:
If you enter the names of translators in this text box, the TDB search is restricted to segments last edited by the specified translators. You have to be careful with this command: Make sure that the translators entered actually exist in the TDBs.
If you enter more than one translator, they must be separated by a semicolon.
· Do not search, if TM search has 100% hit:
If this checkbox is checked, the TDB search is not executed when the TM search has a 100% hit, simply because in this case there is usually no need for a TDB search.
· Case sensitive search:
If this checkbox is checked, the results of a TDB search are searched according to the one of the following options:
▪ Apply to all terms
If this option is active, any term found must have the same lower/uppercase structure as the term in the segment.
For example: If the source segment contains the word "uno” in uppercase and the TDB contains the three terms "uno”, "Uno” and "UNO”, only "uno” will be displayed as TDB search result.
▪ Apply to terms with first letter in Uppercase
If this option is active, any term found with the first letter in Uppercase must have the same lower/uppercase structure as the segment.
For example: If the source segment contains the word "Uno” in uppercase and the TDB contains both "uno” and "Uno”, only "Uno” will be displayed as TDB search result.
▪ Apply to terms in UPPERCASE only
If this option is active, any term found completely in UPPERCASE must also be completely in uppercase in the segment searched.
For example: If the source segment contains the word "UNO” in uppercase and the TDB contains both "uno” and "UNO”, only "UNO” will be displayed as TDB search result.
· Use TDB also as TM:
If this option is checked, the TDB will not only be searched as TDB, but also as TM, that is, the terms in the TDB will be treated as TUs. This can further increase your translation efficiency, for example, when the TDB contains long phrases.
· Language chain searching:
If this option is checked, the search will be extended to find more TUs if the TM contains multi-lingual content. For example, let’s assume that you are translating a text from English to French (EN->FR). If the TM contains TUs in the language combinations EN->IT and IT->FR, where one EN segment is very similar or identical to the segment currently searched, the TM search will usually not be successful because there is no EN->FR dataset in the TM. However, if the language chain searching is active, MetaTexis will look further. And if the IT segments are identical, MetaTexis will actually find the French translation of the Italian text and assign it to the English source text, and an EN->FR hit will be displayed. This search even works across TMs!
Moreover, if the inverse searching is active, the language chain search even works if the language direction are mixed, e.g. MetaTexis will find a match if the TM has the TUs IT->EN and FR->IT.
· Inverse search (the databases must be enabled for inverse searching):
If this option is checked, the TDBs will also be searched for matches with the opposite language direction. This option works only if the database was activated for inverse searching and saving when it was created (see Local MetaTexis Databases). Combined with the language chain searching feature, this opens up amazing possibilities (see above).